Understanding FTTx Technology and Fiber Optic Cables
Unveiling FTTx Technology
Fiber optic technology, also known as FTTx, has revolutionized modern communication networks, offering high-speed data transmission and reliable connectivity. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of FTTx technology and its impact on modern communication networks. By delving into the architecture, challenges, and advantages of fiber optic cables, we can unravel the crucial role they play in shaping our digital world.
Did You Know?
Fiber optic technology enables the transmission of data through thin strands of glass or plastic fibers that carry light signals over long distances with minimal signal loss.
Now we can move on to exploring the architecture of FTTx technology.
Exploring FTTx Architecture
Evolution of FTTx Architecture
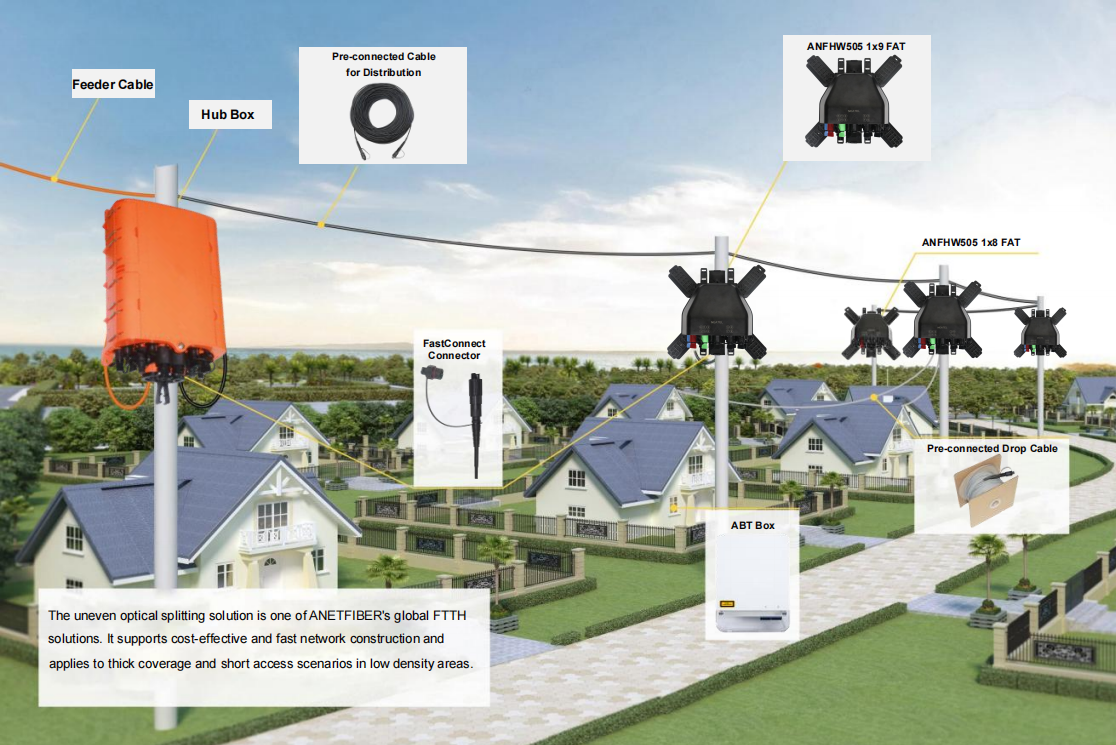
The evolution of FTTx architecture has been a game-changer in the realm of communication networks. Initially, the focus was on Fiber to the Curb (FTTC), which involved bringing fiber optic cables to a curbside cabinet and utilizing copper wires for the final connection to homes. This evolved into Fiber to the Node (FTTN), where fiber optic cables were extended to a central node serving multiple residences. Finally, Fiber to the Home (FTTH) emerged, offering direct fiber optic connections to individual households.
Components of FTTx Architecture
The key components of FTTx architecture include Optical Line Terminal (OLT), Optical Network Terminal (ONT), and Passive Optical Network (PON). The OLT serves as the aggregation point where the data from multiple subscribers is consolidated, while the ONT is installed at the subscriber's premises to convert optical signals into electrical signals for use by customer devices. The PON technology enables the sharing of optical fibers for transmission among multiple subscribers, optimizing infrastructure costs and efficiency.
Did You Know?
The deployment of FTTx architecture has significantly enhanced internet speeds and reliability for end-users, marking a substantial leap forward in communication technology.
Challenges in FTTx Implementation
Infrastructure Deployment Challenges
Deploying the infrastructure required for FTTx implementation presents significant challenges. This includes the installation of fiber optic cables, network equipment, and associated hardware to ensure seamless connectivity. The physical deployment involves meticulous planning, trenching, and installation processes, often requiring coordination with local authorities and utility providers. Moreover, the existing legacy infrastructure may need to be upgraded or replaced to accommodate the new FTTx technology, adding complexity to the deployment process.
Did You Know?
The installation of fiber optic cables for FTTx can involve intricate engineering techniques to ensure minimal signal loss and optimal performance over long distances.
Regulatory and Economic Hurdles
FTTx implementation faces regulatory hurdles related to permits, right-of-way access, and compliance with building codes and environmental regulations. Navigating these legal requirements demands time and resources to secure the necessary approvals for infrastructure deployment. Additionally, economic factors such as initial investment costs, return on investment timelines, and budget constraints pose challenges for widespread FTTx adoption. Addressing these economic hurdles is crucial for ensuring sustainable deployment of fiber optic technology across various geographical regions.
The intricacies of infrastructure deployment and the complexities of regulatory and economic considerations underscore the multifaceted challenges associated with implementing FTTx technology.
Unraveling Fiber Optic Cables
Structure and Function of Fiber Optic Cables
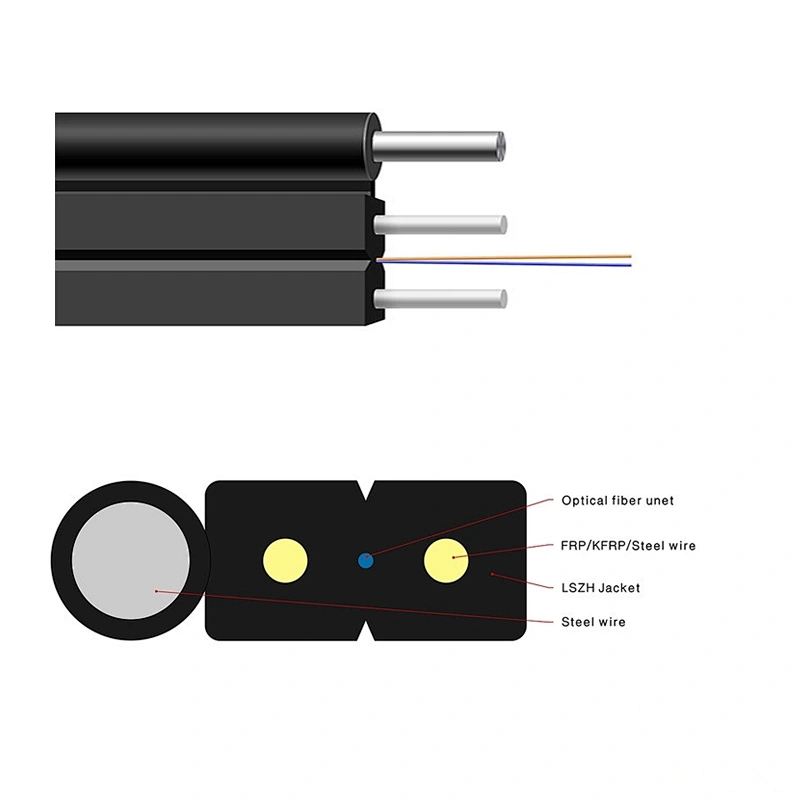
Fiber optic cables are composed of one or more transparent optical fibers enclosed in a protective covering. Each fiber consists of a core, where the light signals travel, surrounded by a cladding layer that reflects the light back into the core. This structure enables the transmission of data through the propagation of light signals along the fiber, allowing for high-speed communication.
The function of fiber optic cables is based on the principle of total internal reflection, where light traveling within the core is continually reflected off the cladding, ensuring minimal signal loss and enabling data to be transmitted over long distances without degradation. This unique structure and function make fiber optic cables ideal for supporting high-bandwidth applications and demanding communication networks.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables offer numerous advantages that contribute to their widespread use in modern communication networks. Firstly, they facilitate high-speed data transmission, surpassing traditional copper-based cables in performance. Additionally, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, providing secure and reliable data transmission even in electrically noisy environments. Moreover, they have a smaller form factor and lighter weight compared to traditional copper cables, making them easier to install and maintain.
The combination of these structural features and functional advantages solidifies fiber optic cables as a cornerstone technology in FTTx architecture, enabling efficient and robust data transmission across various applications and industries.
Contrasting FTTH and FTTN
Understanding FTTH
FTTH, commonly known as fiber to the home, is a cutting-edge technology that directly delivers high-speed internet connections to individual residences. This means that fiber optic cables are extended right into people's homes, providing unparalleled connectivity and network performance. With FTTH, users can experience lightning-fast download and upload speeds, seamless streaming of high-definition content, and robust support for bandwidth-intensive applications. This advanced infrastructure ensures that households have access to reliable and efficient internet services, meeting the demands of modern digital lifestyles.
Exploring FTTN
On the other hand, FTTN, or fiber to the node, involves deploying fiber optic cables to a central point within a neighborhood or community. From this central node, traditional copper-based wiring is then utilized to connect multiple households to the high-speed fiber network. While FTTN still offers significant improvements in internet speed and reliability compared to conventional broadband technologies, it may not match the superior performance and stability provided by FTTH. The distance between the node and individual homes can impact signal strength and data transmission rates in an FTTN setup.
Embracing Fiber Optic Technology
Fiber optic technology, including optical fiber and fiber optics, forms the backbone of modern communication networks. Embracing this advanced technology is essential for meeting the increasing demands of data transmission and connectivity in today's digital landscape.
Advancing Connectivity:
Fiber optic cables enable high-speed data transmission, supporting a wide range of applications from internet services to telecommunication networks.
Understanding the role of fiber optic technology in FTTx architecture is crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable communication systems.
The seamless integration of fiber optic cables contributes to the robustness and scalability of modern communication networks.
In conclusion, embracing fiber optic technology is pivotal for driving innovation and meeting the ever-growing need for fast and secure data transmission.
See Also
The Impact of FTTH, FTTN, FTTC, and FTTP in Fiber Optic Solutions
Understanding Fiber Optic Technology: Explaining FTTH and Its Significance
Unlocking the Advantages of Gigabit Fiber Internet for 2024
The Future of Hybrid Fiber Optic Trunk Cables
Understanding the E2000/APC Fiber Optic Connector for Simplex Multimode OM3
About US
Follow Us
AnetFiber company's main products are indoor and outdoor optical fiber cables, outdoor waterproof pre-connected fiber-to-the-home products, PLC optical fiber splitters, optical fiber jumpers and pigtails, MTP®/MPO high-density big data product solutions, optical fiber field quick connectors and research and development molding, injection molding and production of optical fiber distribution boxes, optical fiber chassis cabinets, the market has expanded to the world, Europe, America, Asia, the Middle East and Latin America.
Address
Shenzhen City, Baoan District, Yanluo Street, Tangxiayong Community, Yangyong Industrial Road, Tonggangda New Energy Vehicle Park 406
Contacts
+86 199 2655 3586