Single Mode vs Multimode Fiber: Which Should You Choose?

Fiber optics have transformed data transmission by utilizing light to convey information. The decision between single-mode and multimode fibers greatly influences performance. Single-mode fibers are ideal for long-distance communication, supporting speeds ranging from 10Gbps to 40Gbps. In contrast, multimode fibers are better suited for shorter distances, providing speeds from 100Mbps to 10Gbps. Choosing the appropriate fiber is crucial for ensuring optimal network performance. Data centers frequently depend on MPO cables, breakout cables, and fiber optic jumpers to enhance connectivity and efficiency. Understanding these options, including the use of MPO connectors and MPO cables, is essential for making informed decisions tailored to your specific needs.
Understanding Fiber Optics
What is Single Mode Fiber?
Definition and Characteristics
Single mode fiber optic cables transmit optical signals through a single path. This design minimizes signal attenuation, ensuring minimal loss during transmission. The core diameter of single mode fibers measures approximately 8 to 10 micrometers. Light waves of different frequencies travel along the same path, maintaining high signal integrity. A laser serves as the light source, which prevents light intensity from diminishing over long distances. Single mode fibers support higher bandwidth capabilities and longer transmission distances.
Typical Applications
Single mode fibers excel in long-haul, high-bandwidth network links. These fibers are ideal for applications like CATV, telecommunication networks, and campus backbones. Large enterprises also benefit from single mode fibers due to their ability to cover extended areas. The maximum distance for single mode fiber can reach 40 kilometers or more. This makes single mode fibers suitable for future-proofing network infrastructure.
What is Multimode Fiber?
Definition and Characteristics
Multimode fiber optic cables support multiple simultaneous light modes. The core diameter of multimode fibers ranges from 50 to 62.5 micrometers. This larger core allows for the transmission of several light paths, which makes multimode fibers suitable for shorter distances. Multimode fibers typically use LED light sources. These fibers offer a more forgiving installation process and are less prone to faults from dirty connections.
Typical Applications
Multimode fibers find their niche in enterprise and data center networks. These fibers are cost-effective for short-distance applications. Multimode fibers support data transmission speeds from 100Mbps to 10Gbps. Data centers often rely on multimode fibers for efficient connectivity within confined spaces. Multimode fibers provide a practical solution for networks where cost-effectiveness is a priority.
Comparative Analysis
Performance Differences
Bandwidth and Distance
Single-mode fiber offers superior bandwidth capabilities. This type of fiber can handle theoretically unlimited bandwidth. Single-mode fiber is ideal for long-distance data transmission. The core design of single-mode fiber minimizes signal loss over extended distances. Multimode fiber supports multiple light paths. This feature makes multimode fiber suitable for shorter distances. Multimode fiber provides adequate bandwidth for local networks.
Signal Quality
Single-mode fiber maintains high signal integrity. The single light path reduces interference and distortion. This ensures a clear and consistent signal over long distances. Multimode fiber experiences more signal attenuation. Multiple light paths can cause modal dispersion. This affects the clarity of the transmitted signal. Multimode fiber is more forgiving in environments with potential interference.
Cost Considerations
Initial Investment
Single-mode fiber requires a higher initial investment. The manufacturing process of single-mode fiber is more complex. Transceivers for single-mode fiber also cost more. Multimode fiber presents a more cost-effective option. The simpler design of multimode fiber reduces production costs. Multimode fiber systems are generally cheaper to install.
Maintenance and Upgrades
Single-mode fiber demands precise installation and maintenance. The delicate nature of single-mode fiber requires careful handling. Upgrades in single-mode systems may involve significant costs. Multimode fiber offers easier maintenance. The larger core diameter allows for less stringent cleaning requirements. Upgrading multimode systems is often more straightforward and affordable.
Decision-Making Factors
Application Needs
Long-Distance vs Short-Distance
Single-mode fiber suits long-distance applications. The design supports minimal signal loss over extended ranges. Single-mode fiber works well for telecommunications and large-scale networks. Multimode fiber fits short-distance needs. The larger core diameter supports multiple light paths. Multimode fiber provides effective solutions for local network setups.
Data Transmission Requirements
Data transmission speed influences fiber choice. Single-mode fiber supports high-speed data transfer. This capability benefits high-bandwidth applications. Multimode fiber offers adequate speeds for smaller networks. Enterprises often use multimode fiber for internal data centers. Both options meet different data transmission needs.
Budget Constraints
Cost-Effectiveness
Budget considerations play a role in fiber selection. Single-mode fiber requires a higher initial investment. The manufacturing process involves more complexity. Multimode fiber presents a cost-effective alternative. The simpler design reduces production costs. Many organizations choose multimode fiber for budget-friendly installations.
Future-Proofing
Future-proofing ensures network longevity. Single-mode fiber offers scalability for future upgrades. The ability to handle increased bandwidth supports long-term growth. Multimode fiber provides flexibility for current needs. Upgrading multimode systems remains straightforward. Organizations must balance immediate costs with future demands.
Practical Applications in Data Centers
Role of MPO Cables
MPO cables play a crucial role in modern data centers. The use of MPO cables simplifies the process of connecting multiple fibers. MPO cables support high-density environments by reducing cable clutter. Data centers benefit from the efficient design of MPO cables. The compact nature of MPO cables allows for easy management and organization.
Use of MPO Connectors
MPO connectors are essential components of MPO cables. MPO connectors enable quick and reliable connections. Data centers rely on MPO connectors for seamless integration. The design of MPO connectors supports high-speed data transmission. MPO connectors ensure minimal signal loss during operation.
Benefits of MPO Cables
MPO cables offer several benefits to data centers. The installation of MPO cables is straightforward and time-saving. MPO cables provide scalability for future network expansions. The flexibility of MPO cables accommodates various configurations. Data centers achieve cost savings with MPO cables due to reduced labor and material costs.
Breakout Cables and Fiber Optic Jumpers
Breakout cables and fiber optic jumpers enhance connectivity in data centers. Breakout cables split a single MPO cable into multiple individual fibers. Fiber optic jumpers connect different network components efficiently. The combination of breakout cables and fiber optic jumpers optimizes network performance.
Functionality in Data Centers
Breakout cables serve a functional purpose in data centers. Breakout cables facilitate the distribution of signals to multiple devices. Fiber optic jumpers bridge connections between equipment racks. Data centers use breakout cables and fiber optic jumpers to streamline operations. The versatility of breakout cables and fiber optic jumpers supports diverse networking needs.
Advantages and Limitations
Breakout cables and fiber optic jumpers offer distinct advantages. The use of breakout cables reduces the need for additional cabling. Fiber optic jumpers provide flexibility in network design. However, breakout cables and fiber optic jumpers have limitations. The complexity of managing breakout cables and fiber optic jumpers requires careful planning. Data centers must consider these factors when implementing breakout cables and fiber optic jumpers.
You must consider several factors when choosing between single-mode and multimode fiber. Single-mode fiber excels in long-distance networks and high-bandwidth applications. This type of fiber offers future-proofing for your network infrastructure. Multimode fiber provides a cost-effective solution for shorter distances. The larger core diameter supports multiple light paths, making it ideal for local networks. Your decision should align with specific application needs and budget constraints. Understanding the characteristics and applications of each fiber type ensures optimal performance for your network.
See Also
What Makes Fiber Optic Splice Closures Essential?
Choosing the Right Data Center Solutions: Key Factors to Consider
Understanding Different Types of MPO Breakout Cables
About US
Follow Us
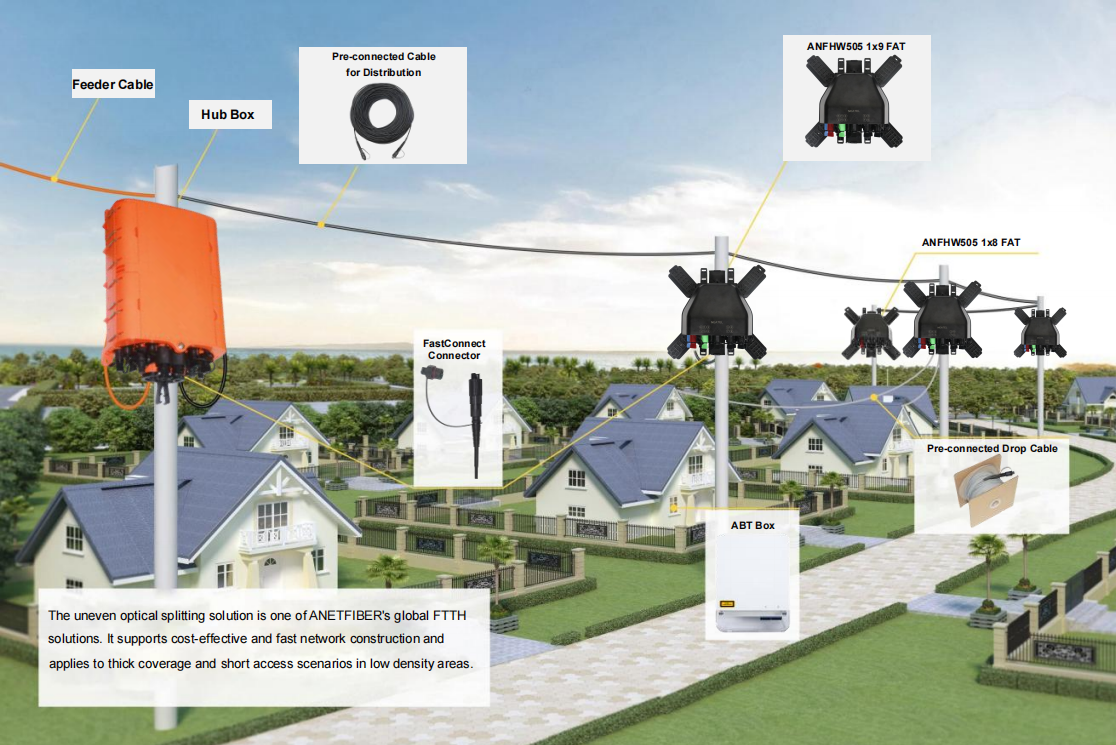
AnetFiber company's main products are indoor and outdoor optical fiber cables, outdoor waterproof pre-connected fiber-to-the-home products, PLC optical fiber splitters, optical fiber jumpers and pigtails, MTP®/MPO high-density big data product solutions, optical fiber field quick connectors and research and development molding, injection molding and production of optical fiber distribution boxes, optical fiber chassis cabinets, the market has expanded to the world, Europe, America, Asia, the Middle East and Latin America.
Address
Shenzhen City, Baoan District, Yanluo Street, Tangxiayong Community, Yangyong Industrial Road, Tonggangda New Energy Vehicle Park 406
Contacts
+86 199 2655 3586