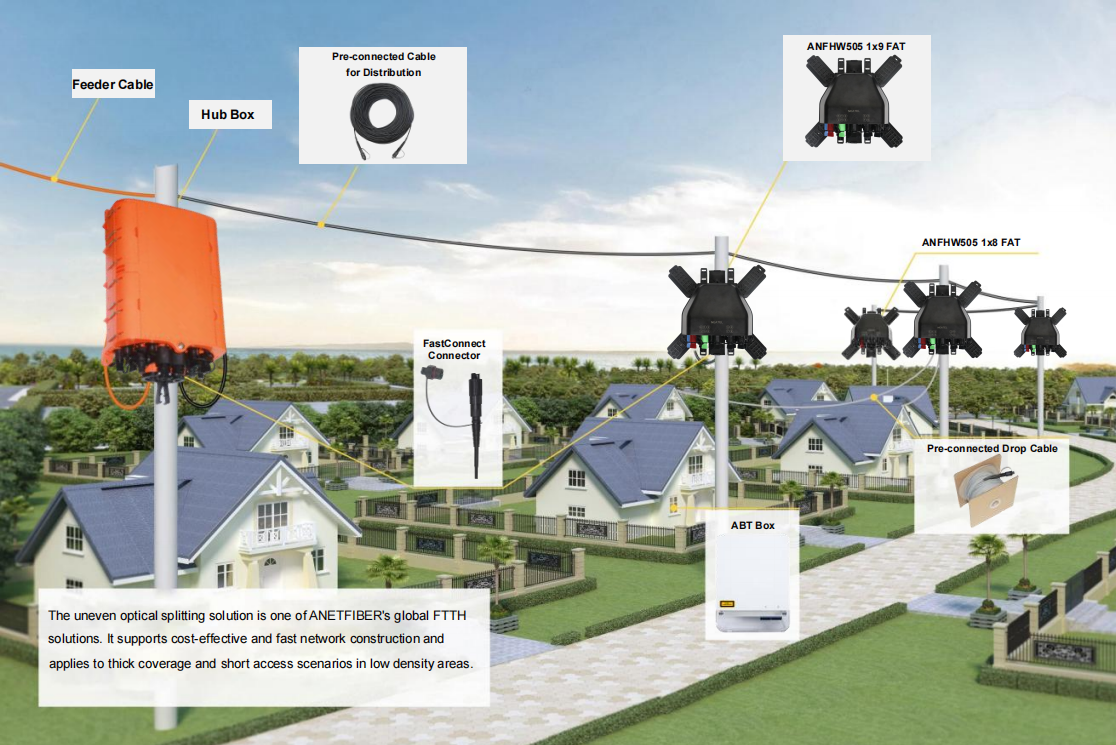
What Makes Fiber Splitters Essential in Networks

Fiber optic networks, utilizing fiberopticcable, have become the backbone of modern telecommunications, enabling high-speed data transmission over long distances. The efficiency of these networks relies heavily on the quality and functionality of their components, particularly the fiber optic splitters. These devices distribute the opticalsignal from a single source to multiple destinations, ensuring seamless data transfer. Fiber optic splitters, such as plcsplitter and fbt splitters, are crucial in maintaining signal integrity, with considerations for IL (Insertion Loss) and RL (Return Loss). Their application in various network configurations, including abssplitter, cassettesplitter, and blocklesssplitter, enhances network performance and reliability.
Understanding Fiber Splitters
What are Fiber Splitters?
Definition and Basic Function
Fiber splitters serve as essential components in optical networks. These devices divide an optical signal from a single input into multiple outputs. This process enables efficient signal distribution across various network points. Fiber splitters function without the need for external power sources. The design incorporates passive materials like quartz substrate and stainless steel. This ensures durability and reliability in network operations.
Role in Fiber Optic Networks
Fiber splitters play a crucial role in enhancing network efficiency. They allow a single optical signal to reach multiple destinations. This capability supports the expansion of network capacity. Fiber splitters also maintain signal integrity by minimizing losses. This ensures high-quality data transmission over long distances. The use of fiber splitters is widespread in passive optical networks (PONs). These networks benefit from the ability to distribute signals to numerous end-users.
Types of Fiber Splitters
FBT (Fused Biconical Taper) Splitters
FBT splitters utilize a traditional manufacturing process. This involves fusing fibers together and tapering them to achieve the desired split ratio. FBT splitters support a range of operating wavelengths from 1260nm to 1650nm. This versatility makes them suitable for various applications. However, FBT splitters tend to be more expensive at higher split ratios. The complexity of manufacturing and the use of non-traditional materials contribute to this cost. Despite these challenges, FBT splitters offer higher spectral uniformity. Losses remain consistent across different wavelengths.
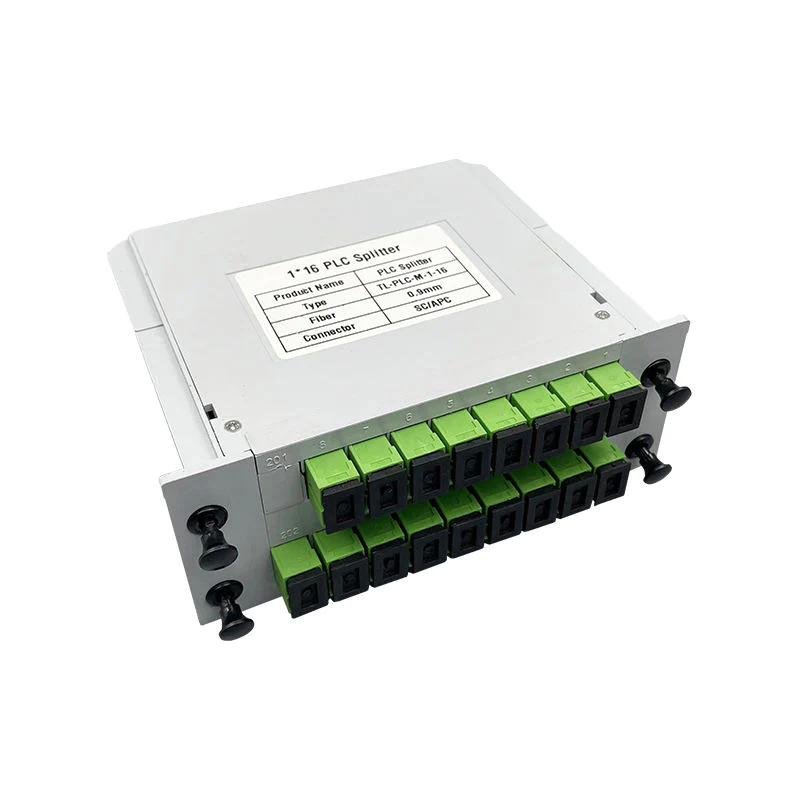
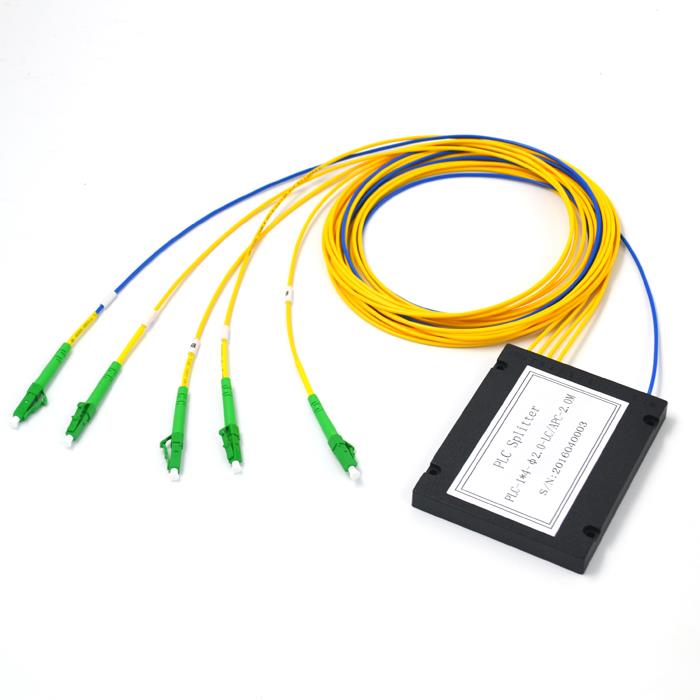
PLC (Planar Lightwave Circuit) Splitters
PLC splitters provide a modern solution for light distribution. These devices use silica glass chips to split optical signals. PLC splitters offer several advantages over FBT splitters. They exhibit higher port-to-port uniformity and support a wider wavelength range. PLC splitters also accommodate higher splitting ratios, reaching up to 1x64. This capability makes them ideal for large-scale network deployments. Additionally, PLC splitters demonstrate lower insertion loss and polarization-dependent loss. This ensures stable and reliable performance in diverse network environments.
How Fiber Splitters Work
Signal Splitting Process
Optical Signal Division
Fiber splitters perform a critical function in optical networks by dividing an incoming opticalsignal into multiple streams. This division process involves the use of passive components that do not require external power. The materials used, such as quartz substrate and stainless steel, ensure durability and reliability. The ability to split signals efficiently is essential for maintaining high-speed data transmission across various network points.
Signal Distribution to Multiple Outputs
Once the opticalsignal is divided, fiber splitters distribute the signal to multiple outputs. This distribution capability supports network scalability by allowing a single signal source to reach numerous destinations. The process ensures that each output receives a portion of the original signal, facilitating seamless data transfer in applications like telecommunications and data centers. Optical splitters play a pivotal role in Passive Optical Networks (PONs), enabling shared fiber access and reducing the need for extensive cabling.
Technical Specifications
Split Ratio
The split ratio is a key specification in fiber splitters, determining how the opticalsignal is divided among the outputs. Common split ratios include 1x2, 1x4, 1x8, up to 1x64, depending on the network requirements. A higher split ratio allows more outputs from a single input, which is beneficial for large-scale deployments. However, increasing the split ratio can lead to higher IL, affecting signal strength at each output.
Insertion Loss (IL) and Return Loss (RL)
Insertion Loss (IL) and Return Loss (RL) are critical parameters in evaluating fiber splitter performance. IL measures the loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of the splitter in the network. Lower IL values indicate better efficiency, ensuring minimal signal degradation. Return Loss (RL) quantifies the amount of signal reflected back towards the source. Higher RL values signify better performance, as less signal is lost due to reflections. Both IL and RL are essential for maintaining signal integrity and ensuring reliable data transmission.
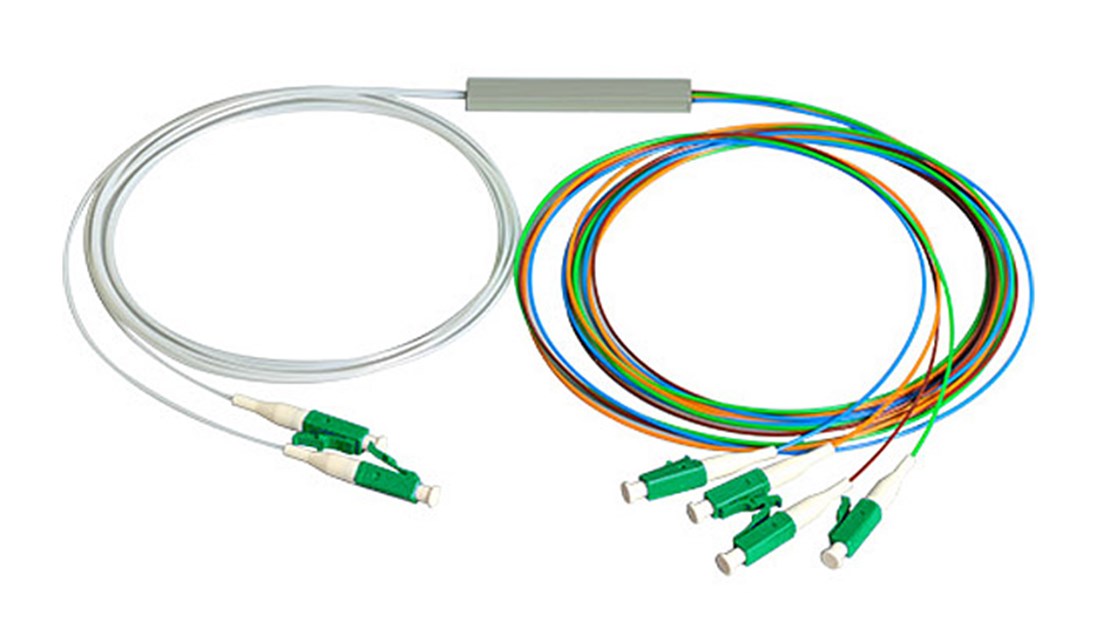
Benefits of Using Fiber Splitters
Network Scalability
Expanding Network Capacity
Fiber splitters enhance network scalability by allowing a single optical signal to serve multiple endpoints. This capability eliminates the need for individual lines for each connection, which would be technically challenging and costly. Networks can efficiently expand their capacity using splitters, accommodating more users without extensive infrastructure changes. The ability to share a single fiber optic cable across multiple locations promotes efficient bandwidth distribution.
Supporting Multiple Connections
Fiber splitters support multiple connections by dividing an optical signal into several paths. This feature enables networks to connect numerous end-users to a central office or service provider. Splitters facilitate the deployment of passive optical networks (PONs), which efficiently distribute signals to various destinations. The flexibility of splitters supports different network architectures, such as point-to-multipoint configurations, allowing easy expansion to meet growing demands.
Cost Efficiency
Reducing Infrastructure Costs
Fiber splitters significantly reduce infrastructure costs by minimizing the need for dedicated cables. The shared use of a single fiber optic cable across multiple users or locations results in substantial cost savings. Splitters allow networks to grow without the expense of additional cabling, making them a cost-effective solution for expanding network reach. The use of splitters in centralized or distributed PON architectures further optimizes resource allocation.
Minimizing Maintenance Expenses
Fiber splitters contribute to lower maintenance expenses by simplifying network design. The reduced need for extensive cabling decreases potential points of failure, leading to fewer maintenance requirements. Splitters offer a reliable solution for distributing signals, ensuring consistent performance with minimal intervention. The durability of materials used in splitters, such as quartz substrate and stainless steel, enhances their longevity and reduces the frequency of repairs.
Applications of Fiber Splitters
Telecommunications
Enhancing Broadband Services
Fiber splitters play a pivotal role in telecommunications by enhancing broadband services. Network providers utilize fiber splitters to distribute optical signals efficiently across multiple endpoints. This distribution ensures that each user receives a consistent and high-quality connection. The use of fiber splitters reduces the need for extensive cabling, which simplifies network infrastructure. This approach allows for cost-effective expansion of broadband services to more areas.
Supporting High-Speed Internet
High-speed internet relies heavily on the effective use of fiber splitters. These devices enable the delivery of fast and reliable internet connections to numerous users simultaneously. By dividing optical signals into multiple streams, fiber splitters support the increasing demand for bandwidth. This capability is essential for accommodating activities such as video streaming, online gaming, and cloud computing. The implementation of fiber splitters in networks ensures that users experience minimal latency and uninterrupted service.
Data Centers
Optimizing Data Distribution
Data centers benefit significantly from the integration of fiber splitters. These components optimize data distribution by allowing efficient signal routing to various servers and storage units. Fiber splitters facilitate the management of large volumes of data traffic within data centers. This optimization enhances the overall performance and speed of data processing operations. The strategic placement of fiber splitters in data center architectures contributes to improved resource allocation and system efficiency.
Improving Network Reliability
Network reliability in data centers improves with the use of fiber splitters. These devices ensure that data signals are consistently delivered to all necessary points within the network. Fiber splitters reduce the risk of signal loss or degradation, which can lead to downtime or data errors. The robust construction of fiber splitters, using materials like quartz substrate, enhances their durability and longevity. This reliability is crucial for maintaining continuous and dependable data center operations.

Types of Splitter Configurations
ABS Splitter
ABS splitters are integral components in fiber optic networks. These devices feature a robust ABS plastic casing that provides excellent protection for internal fibers. The design ensures durability and reliability in various environmental conditions. ABS splitters are commonly used in applications like FTTH networks and PONs. These splitters distribute signals efficiently to multiple destinations, ensuring high-quality data transmission. The compact design of ABS splitters allows easy installation in limited spaces, making them ideal for dense network environments.
Cassette Splitter
Cassette splitters offer a unique design that enhances network management. These devices come in a modular cassette form, allowing easy integration into existing network infrastructures. The design facilitates quick and efficient connections, reducing installation time. Cassette splitters are widely used in telecommunication systems and cable TV networks. The modular nature of these splitters supports flexible network configurations. This flexibility enables network operators to adapt to changing demands without extensive reconfiguration. Cassette splitters ensure reliable signal distribution, maintaining network performance and integrity.
Blockless Splitter
Blockless splitters provide significant advantages in fiber optic networks. These devices feature a compact and lightweight design, eliminating the need for a bulky protective housing. The absence of a block makes these splitters cost-effective and easy to deploy. Blockless splitters are suitable for centralized or distributed optical distribution boxes. Their versatility allows use in various applications, including FTTH networks and telecommunication systems. The design ensures minimal insertion loss, maintaining signal quality across multiple outputs. Blockless splitters enhance network scalability by supporting numerous connections from a single input source.
Fiber splitters hold significant importance in modern network infrastructures. These components enhance network capacity by dividing a single optical fiber into multiple fibers, allowing efficient resource sharing among users. Fiber splitters play a crucial role in passive optical networks (PONs) and fiber optic systems, enabling simultaneous data transmission to various endpoints. Their application extends to fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) networks and cable TV systems. Network planners should consider incorporating fiber splitters to ensure flexibility and scalability. The use of fiber splitters supports network growth without excessive port usage or additional fiber lines.
See Also
What Makes Fiber Optic Splice Closures Essential?
Choosing the Right Data Center Solutions: Key Factors to Consider
Understanding Different Types of MPO Breakout Cables
About US
Follow Us
AnetFiber company's main products are indoor and outdoor optical fiber cables, outdoor waterproof pre-connected fiber-to-the-home products, PLC optical fiber splitters, optical fiber jumpers and pigtails, MTP®/MPO high-density big data product solutions, optical fiber field quick connectors and research and development molding, injection molding and production of optical fiber distribution boxes, optical fiber chassis cabinets, the market has expanded to the world, Europe, America, Asia, the Middle East and Latin America.
Address
Shenzhen City, Baoan District, Yanluo Street, Tangxiayong Community, Yangyong Industrial Road, Tonggangda New Energy Vehicle Park 406
Contacts
+86 199 2655 3586