Exploring the Different Types of Fiber Optic Splice Closures in 2024
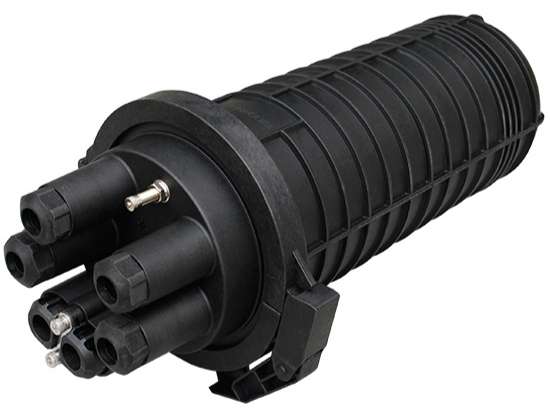

Unveiling Fiber Optic Splice Closures
Fiber optic splice closures are essential components in fiber optic networks, serving a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and reliability of optical connections. These closures provide protection and organization for fiber optic splices, which join two or more optical fibers together to create a continuous signal transmission path.
Network engineers understand the significance of splice closures as they enable seamless connectivity and prevent signal loss or degradation. By securely housing spliced fibers, these enclosures safeguard them from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and physical damage.
In this blog, we will delve into the different types of fiber optic splice closures available in 2024. By exploring their features, applications, installation process, maintenance requirements, and future trends, we aim to provide technical professionals with valuable insights into optimizing their fiber optic networks.
Delving into Fiber Optic Splicing
Fiber optic splicing is a critical process in network installations that involves joining two or more optical fibers together to create a continuous transmission path. This technique plays a vital role in ensuring seamless connectivity and optimal performance in fiber optic networks.
Understanding Fiber Optic Splicing
Fiber optic splicing refers to the process of permanently joining two optical fibers together, either by fusion splicing or mechanical splicing. It is an essential technique used in various applications, including telecommunications, data centers, and cable TV networks.
The importance of fiber optic splicing lies in its ability to create low-loss connections between fibers. By eliminating the need for connectors, which can introduce signal loss and reflection, spliced fibers provide a more reliable and efficient means of transmitting data over long distances.
Different Methods of Fiber Optic Splicing
There are two primary methods of fiber optic splicing: fusion splicing and mechanical splicing.
Fusion Splicing
Fusion splicing involves using heat to melt the ends of two optical fibers together, creating a permanent bond. This method offers several benefits, including low insertion loss, high tensile strength, and excellent long-term stability. Fusion splices also have lower reflectance levels compared to mechanical splices, making them ideal for high-speed data transmission.
Mechanical Splicing
Mechanical splicing involves aligning and mechanically securing two fiber ends using specialized connectors or splice sleeves. While it may not achieve the same level of performance as fusion splicing, mechanical splices offer advantages such as ease of installation, reusability, and lower equipment costs. They are commonly used in situations where quick repairs or temporary connections are required.
When comparing fusion splicing and mechanical splicing techniques, it's important to consider factors such as cost, installation time, durability requirements, and network specifications. Each method has its own strengths and applications depending on the specific needs of the fiber optic network.
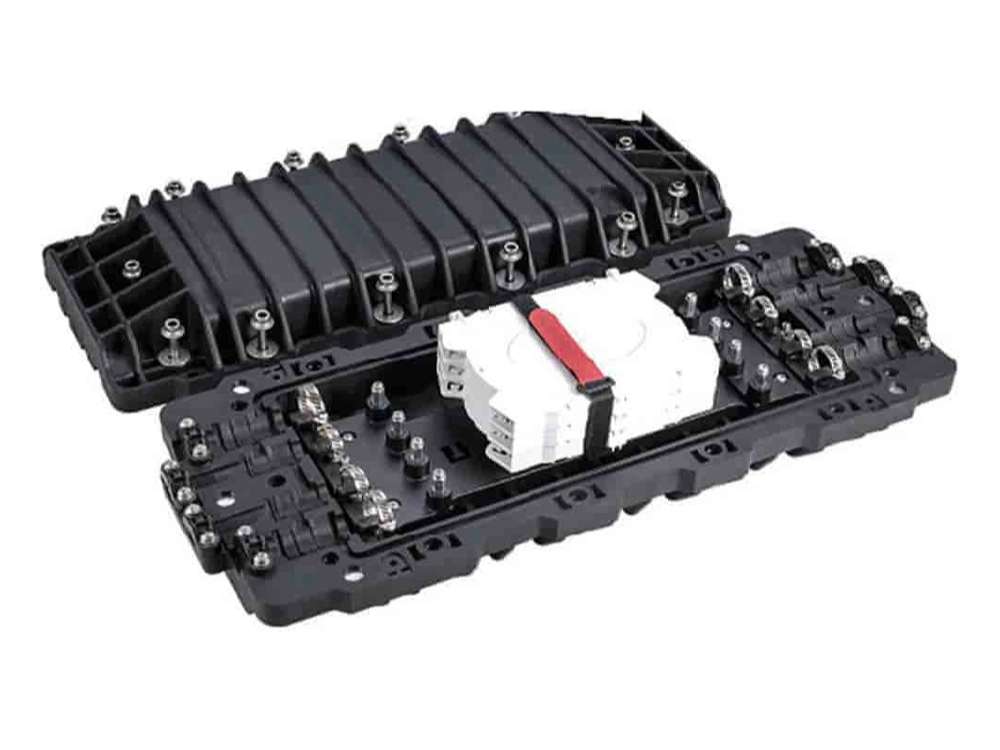

Comparing Types of Fiber Optic Splice Closures
Fiber optic splice closures are protective enclosures designed to house and protect fiber optic splices. They play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and performance of fiber optic networks. It is essential to understand the different types of splice closures available to select the most suitable one for specific applications.
Overview of Fiber Optic Splice Closures
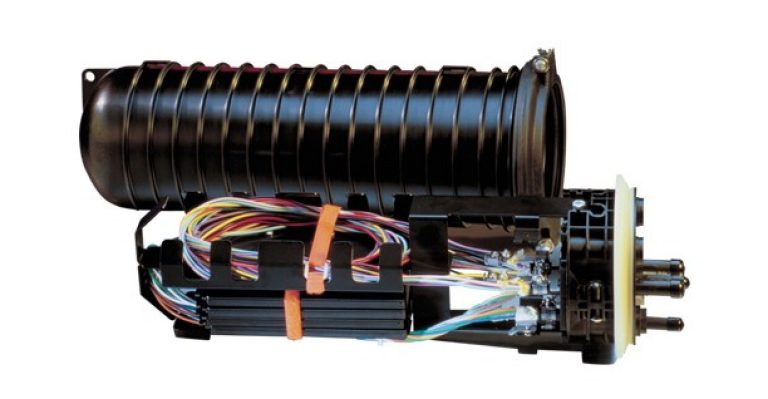
A fiber optic splice closure is a robust enclosure that provides protection against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and physical damage. Its primary purpose is to ensure the reliability and longevity of fiber optic connections by securely housing spliced fibers.
Selecting the right splice closure is vital as it directly impacts network performance and maintenance. Different types of closures offer various features, sizes, and installation options, catering to diverse network requirements.
Types of Fiber Optic Splice Closures
Dome Closures: Dome closures are compact enclosures designed for aerial or underground installations. They provide excellent protection against harsh weather conditions and are suitable for both single fiber and ribbon splicing applications.
Inline Closures: Inline closures are elongated enclosures that allow easy access to individual fibers within a cable. They are commonly used in long-haul fiber optic networks where multiple splices need to be accommodated.
Horizontal Closures: Horizontal closures are typically used in indoor installations such as data centers or equipment rooms. These closures offer easy access for maintenance purposes and can accommodate a large number of splices.
By comparing these different types of splice closures, network engineers can determine which type best suits their specific needs based on factors like installation location, capacity requirements, accessibility, and environmental conditions.
Ensuring Smooth Operations: Installation, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting
Proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting are crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of fiber optic splice closures within a network of fiber cables. By following best practices and guidelines, network engineers can optimize the performance and longevity of their fiber optic infrastructure.
Installation Process of Fiber Optic Splice Closures
Installing fiber optic splice closures requires careful planning and execution to ensure reliable connections. Here is a step-by-step guide for installing splice closures:
Select an appropriate location: Choose a suitable location that provides easy access for future maintenance and protects the closure from environmental factors.
Prepare the enclosure: Ensure that the splice closure is clean and free from any debris or contaminants before installation.
Mount the closure: Securely mount the splice closure using appropriate brackets or mounting hardware as per manufacturer guidelines.
Prepare fiber cables: Strip, clean, and prepare the fiber cables for splicing according to industry standards.
Splice fibers: Use fusion splicing or mechanical splicing techniques to join fibers together inside the closure.
Organize cables: Properly manage cable routing within the enclosure to maintain neatness and prevent damage to splices.
Close and seal the enclosure: Ensure that all openings are securely closed and sealed to protect against moisture or dust ingress.
Considerations for proper installation include selecting compatible closure types, following safety protocols, maintaining proper bend radius for fiber cables, and adhering to local regulations.
Maintenance of Fiber Optic Splice Closures
Regular maintenance is essential for preserving optimal performance in optical fiber networks. Here are some key maintenance procedures:
Regular inspection: Periodically inspect splice closures for any signs of damage, loose connections, or environmental degradation.
Cleaning procedures: Clean connectors, adapters, and enclosure surfaces using lint-free wipes and approved cleaning solutions to remove dirt or contaminants that may affect signal quality.
Preventive maintenance practices: Implement preventive measures such as monitoring environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), conducting periodic testing (OTDR), and documenting network changes or repairs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Splice Closures
When encountering issues with fiber optic splice closures, it's important to identify problems promptly and resolve them efficiently:
Identifying common problems: Common issues include signal loss, excessive reflectance, improper cable management, connector damage, or environmental factors affecting performance.
Troubleshooting tips:
Inspect connectors for cleanliness and damage.
Check cable routing for proper strain relief.
Verify fusion splices or mechanical connections.
Monitor power levels using optical power meters.
Conduct OTDR testing to locate faults or breaks in fibers.
By following these installation procedures, performing regular maintenance tasks, and effectively troubleshooting issues with splice closures, network engineers can ensure smooth operations within their optical fiber networks.
Future Trends in Fiber Optic Splice Closures
As technology continues to advance, fiber optic splice closures are also evolving to meet the demands of modern networks. These advancements bring forth exciting possibilities for enhanced network efficiency and scalability.
Advancements in Fiber Optic Splice Closures
Emerging technologies and innovations in splice closures are paving the way for improved performance and reliability. Manufacturers are exploring new materials, designs, and manufacturing techniques to create more robust and efficient splice closures. These advancements aim to reduce insertion loss, increase tensile strength, and enhance environmental protection.
The impact of future trends on network efficiency and scalability is significant. With advanced splice closures, network engineers can achieve higher data transmission rates, longer distances, and greater bandwidth capacity. This enables the seamless integration of emerging technologies such as 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing into fiber optic networks.
Anticipated Developments in Splice Closure Design
Future developments in splice closure design focus on compactness, modularity, and advanced features. Compact designs allow for easier installation in space-constrained environments while maintaining optimal performance. Modular splice closures offer flexibility by allowing easy expansion or reconfiguration as network needs evolve.
Integration of advanced features such as intelligent monitoring systems, self-healing capabilities, or automated maintenance routines further enhances the performance and reliability of fiber optic networks. These features enable proactive fault detection, faster troubleshooting, and reduced downtime.
By staying informed about these anticipated developments in splice closure design, network engineers can plan for future infrastructure upgrades that align with industry trends and ensure their networks remain at the forefront of technological advancements.
Future Trends in Fiber Optic Splice Closures
Fiber optic splice closures are constantly evolving to keep pace with technological advancements. As networks continue to grow and demand for higher performance increases, staying updated with the latest trends in splice closure design and functionality is crucial for network engineers.
The future of fiber optic splice closures holds great potential for improved network performance and scalability. Advancements in materials, designs, and features will enable faster data transmission, longer distances, and greater bandwidth capacity. Compact and modular designs will provide flexibility for network expansion or reconfiguration. Integration of advanced features like intelligent monitoring systems will enhance fault detection and maintenance efficiency.
By embracing these future trends, network engineers can ensure their fiber optic networks remain efficient, reliable, and ready to support emerging technologies. The continuous evolution of fiber optic splice closures promises a bright future for enhanced network connectivity and seamless data transmission.
See Also
The Future of Fiber Optic PLC Technology: Exploring Couplers, Splitters, WDM's, and More
Boost Network Performance with Multimode OM4 MPO to MPO Fiber Trunk Cable
Enhancing Fiber Preconnection Solutions with Precon Optic Fastconnect MPO Breakout Cable Assemblies
The Future of Fiber Preconnection Solutions: Exploring MTP-LC Duplex 12cores Trunk Cable Patchcord
About US
Follow Us
AnetFiber company's main products are indoor and outdoor optical fiber cables, outdoor waterproof pre-connected fiber-to-the-home products, PLC optical fiber splitters, optical fiber jumpers and pigtails, MTP®/MPO high-density big data product solutions, optical fiber field quick connectors and research and development molding, injection molding and production of optical fiber distribution boxes, optical fiber chassis cabinets, the market has expanded to the world, Europe, America, Asia, the Middle East and Latin America.
Address
Shenzhen City, Baoan District, Yanluo Street, Tangxiayong Community, Yangyong Industrial Road, Tonggangda New Energy Vehicle Park 406
Contacts
+86 199 2655 3586