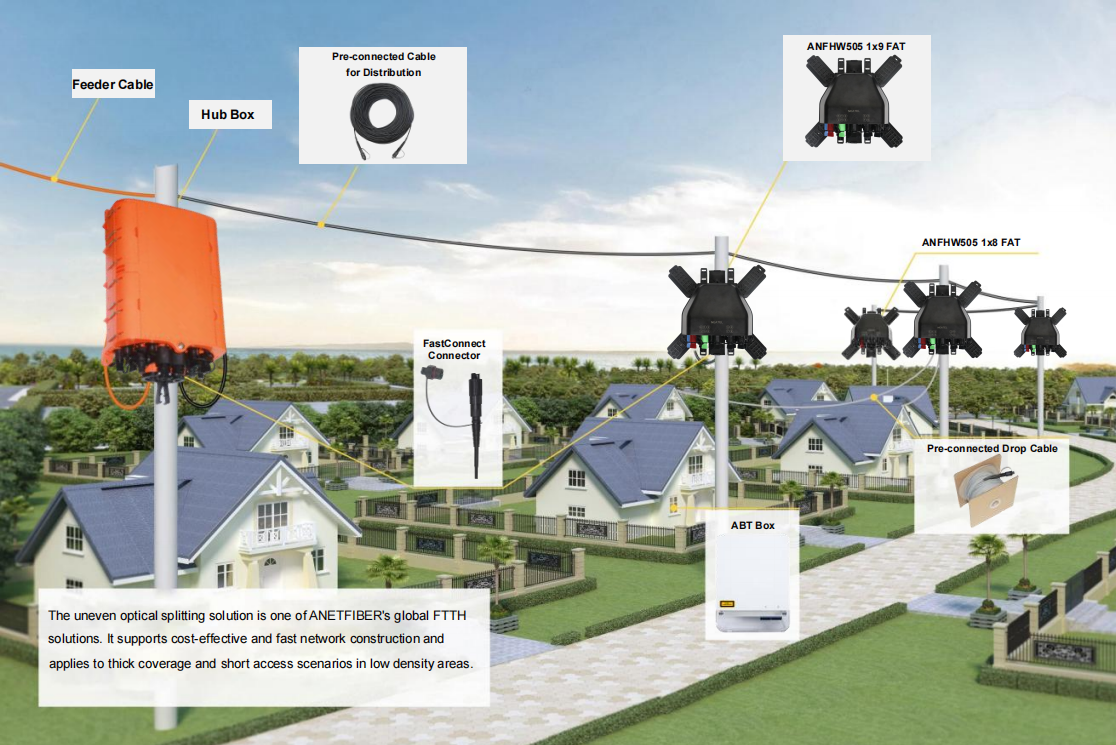
Unveiling the Differences: FBT vs PLC Splitters in Optical Transmission
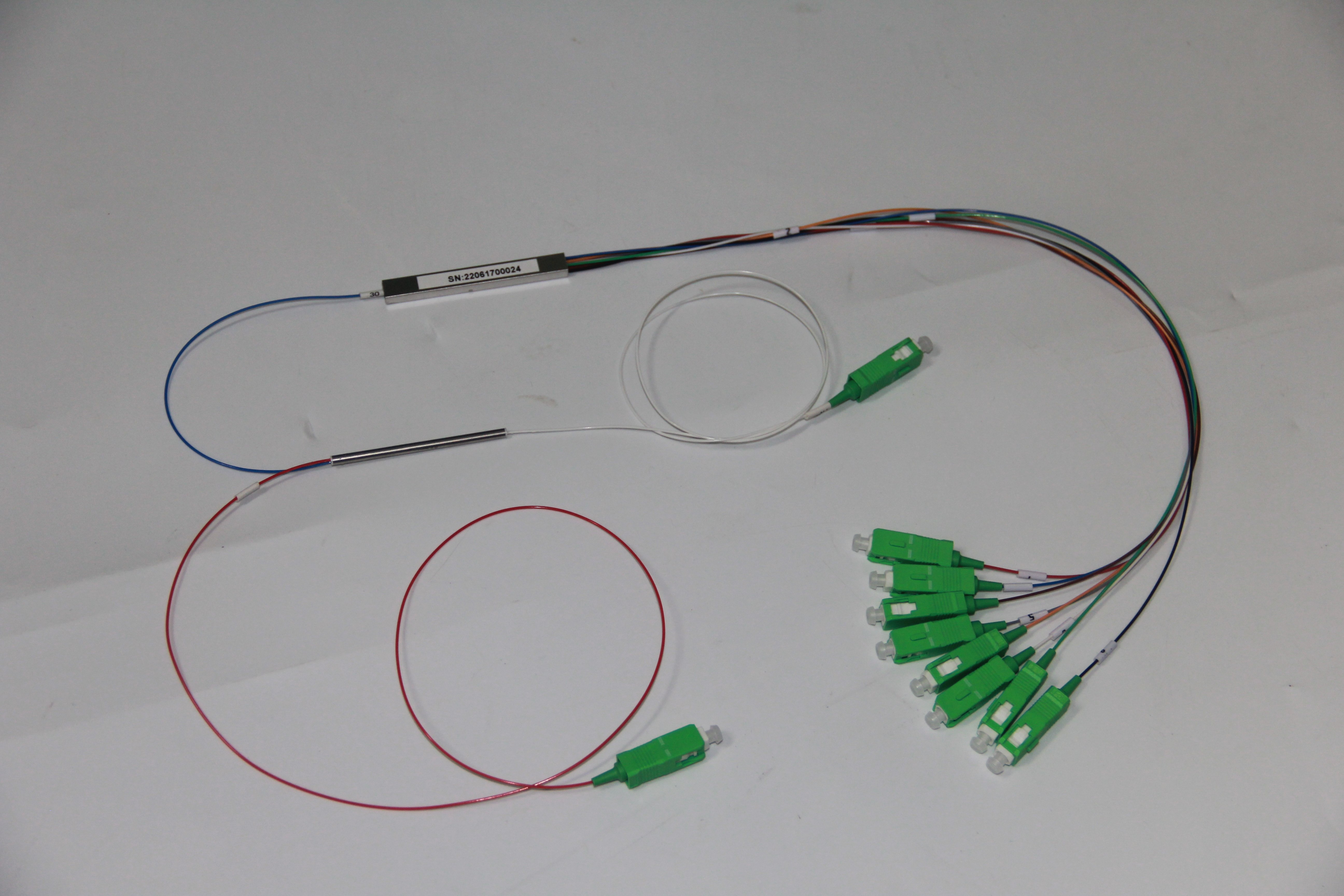
In the realm of fiber optic networks, the significance of optical splitters cannot be overstated. These fiber optic components play a pivotal role in dividing optical signals, ensuring seamless data transmission. Within this domain, two prominent players stand out: the Fused Biconic Taper (FBT) splitter and the Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) splitter. While the Fused Biconic Taper (FBT) splitter relies on a traditional fused biconical tapering process, PLC splitters harness cutting-edge planar lightwave circuit technology for signal division. The primary aim of this blog is to meticulously compare these two stalwarts in the optical transmission arena.
Fused Biconic Taper (FBT) Splitters
Construction and Working Principle
The Fused Biconic Taper (FBT) splitter is meticulously crafted through a traditional tapered coupler process. This method involves bundling two or more optical fibers, subjecting them to high temperatures for melting, closely monitoring the real-time splitting ratio, and finally solidifying the tapered region on a quartz substrate using curing glue.
Advantages
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the primary advantages of the FBT Optical Splitter lies in its cost-effectiveness. The production process is straightforward, allowing for easy material acquisition and low overall costs. This makes it an attractive option for various optical network setups.
Simplicity
In terms of design and functionality, simplicity is a key feature of the FBT splitter. Its uncomplicated construction makes it easy to deploy and maintain within fiber optic networks, offering efficiency without unnecessary complexities.
Disadvantages
Prone to Inconsistencies
Despite its benefits, the FBT splitter is susceptible to inconsistencies in performance. These variations can impact signal quality and may require additional monitoring to ensure optimal operation.
Limited Splitting Ratio
Another drawback of the FBT splitter is its limitation in splitting ratio support. This factor can restrict its application in scenarios requiring precise division of optical signals across multiple outputs.
Applications
FBT Optical Splitters find extensive utilization in fiber optic networks, serving as crucial components for efficient signal distribution. The versatility of these splitters allows them to be deployed in various scenarios, showcasing their adaptability and reliability.
Use in Fiber Optic Networks
Facilitates seamless transmission of optical signals within intricate fiber optic setups.
Enables the division of incoming signals into multiple outputs with precision and efficiency.
Ensures optimal data flow by maintaining signal integrity throughout the network.
Specific Scenarios
FTTH Networks: FBT splitters play a vital role in Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) networks, ensuring reliable connectivity for end-users.
Outdoor Splitting Points: Ideal for outdoor installations, these splitters offer robust performance in challenging environmental conditions.
Customer-Specific Configurations: Tailored configurations like 1x4, 1x8, or 1x16 cater to specific network requirements with ease.
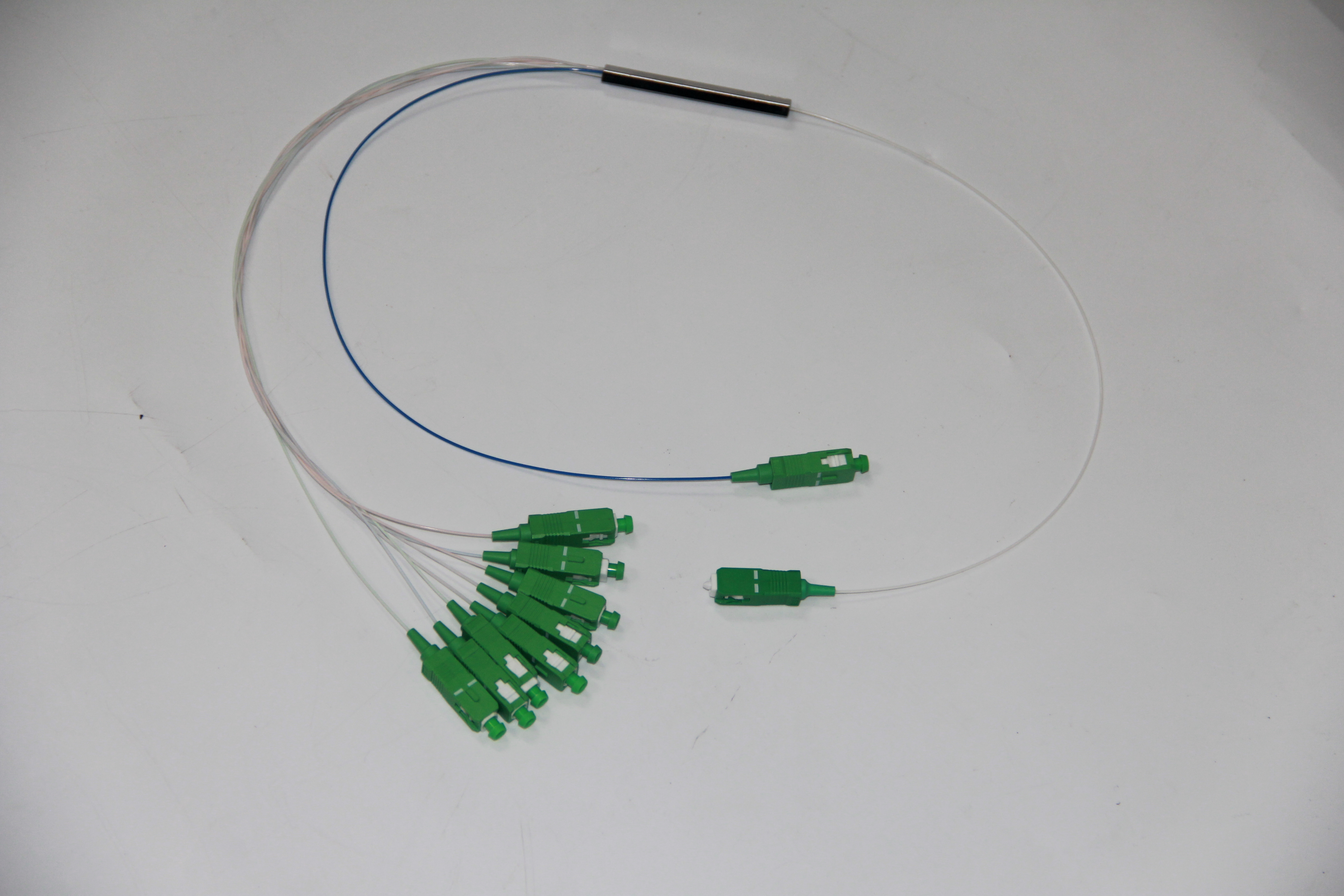
Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) Splitters
Construction and Working Principle
The Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) splitter stands out for its innovative technology, utilizing a planar lightwave circuit design. This cutting-edge approach involves integrating optical waveguides onto a flat substrate, allowing for precise signal splitting with minimal loss. The signal splitting mechanism in PLC splitters is based on the efficient propagation of light waves through these integrated waveguides, ensuring accurate division of optical signals.
Advantages
High Precision
A key advantage of PLC splitters is their exceptional precision in signal splitting. The integrated waveguide structure enables consistent and accurate division of optical signals, maintaining signal integrity across multiple outputs. This high level of precision makes PLC splitters ideal for applications requiring reliable data transmission.
Wide Splitting Ratio
Another notable benefit of PLC splitters is their support for wide splitting ratios. Unlike traditional FBT splitters that are limited in their splitting capabilities, PLC splitters can efficiently divide optical signals into multiple outputs with varying ratios. This flexibility in splitting ratios enhances the versatility and adaptability of PLC splitters in diverse network setups.
Disadvantages
Higher Cost
One drawback associated with PLC splitters is their higher cost compared to FBT splitters. The advanced technology and intricate manufacturing process involved in creating PLC splitters contribute to their elevated price point. While the initial investment may be higher, the long-term benefits of precision and efficiency often justify the cost for organizations prioritizing performance.
Complexity
The complexity of PLC splitter design can pose challenges during deployment and maintenance. The intricate integration of optical waveguides requires specialized expertise for installation and troubleshooting. This complexity adds a layer of technical sophistication that may require additional training or resources for effective management within fiber optic networks.
Applications
Use in Fiber Optic Networks
In the realm of fiber optic networks, the deployment of FBT Optical Splitters plays a pivotal role in ensuring seamless data transmission. These splitters are fundamental components that facilitate the efficient distribution of optical signals within intricate network setups. Their cost-effectiveness and simplicity make them an attractive choice for various applications within fiber optic networks. By enabling the division of incoming signals into multiple outputs with precision and efficiency, FBT Optical Splitters contribute to maintaining signal integrity throughout the network.
Facilitates seamless transmission of optical signals within intricate fiber optic setups.
Enables the division of incoming signals into multiple outputs with precision and efficiency.
Ensures optimal data flow by maintaining signal integrity throughout the network.
In specific scenarios such as FTTH Networks, these splitters ensure reliable connectivity for end-users. Moreover, their suitability for Outdoor Splitting Points showcases robust performance even in challenging environmental conditions. Additionally, tailored configurations like 1x4, 1x8, or 1x16 cater to specific network requirements with ease, highlighting the adaptability and versatility of FBT Optical Splitters in diverse applications.
Comparison of FBT and PLC Splitters
Performance
Signal Quality
In optical transmission, Signal Quality is a critical factor that directly impacts the efficiency of data transfer. When comparing FBT and PLC splitters, it is evident that both technologies excel in maintaining high signal quality throughout the network. The PLC splitter ensures minimal loss during signal division, guaranteeing that the transmitted data remains intact and clear. On the other hand, the FBT splitter also upholds signal integrity by efficiently splitting optical signals without compromising on quality.
Splitting Ratio
The Splitting Ratio refers to the proportion in which an incoming optical signal is divided into multiple outputs. In this aspect, PLC splitters offer a wide range of splitting ratios, providing flexibility in distributing signals based on specific network requirements. With support for up to 64 channels, PLC splitters cater to diverse applications where precise division is essential. Conversely, FBT splitters, while efficient in splitting signals, have limitations in their splitting ratio capabilities. This can impact their suitability for scenarios demanding extensive signal distribution across multiple outputs.
Cost
Initial Investment
When considering the Initial Investment, organizations must weigh the cost implications of deploying either an FBT or PLC splitter within their network infrastructure. While FBT splitters are known for their cost-effectiveness due to simpler manufacturing processes, PLC splitters often require a higher initial investment. The advanced technology and intricate design of PLC splitters contribute to their elevated price point compared to traditional FBT counterparts.
Maintenance
In terms of ongoing maintenance requirements, both FBT and PLC splitters have distinct considerations. The robust construction of FBT splitters makes them relatively easy to maintain, requiring minimal intervention once deployed in a network setup. On the other hand, the integrated nature of components in PLC splitters may necessitate specialized expertise for maintenance tasks. While initial maintenance costs for PLC technology may be higher, its long-term reliability and precision often justify these expenses for organizations prioritizing performance and efficiency.
Suitability for Different Applications
Small-Scale Networks
For small-scale networks with limited signal distribution needs, both FBT and PLC splitters can effectively serve connectivity requirements. However, the choice between these technologies depends on factors such as budget constraints and scalability options. Organizations operating small-scale networks may find the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of FBT splitters appealing for their connectivity solutions.
Large-Scale Networks
In large-scale network environments where extensive signal distribution is paramount, the precision and wide splitting ratios offered by PLC technology become advantageous. The ability of PLC splitters to efficiently divide optical signals across numerous outputs makes them ideal for complex network setups requiring high-performance data transmission capabilities. While the initial investment may be higher for large-scale deployments, the long-term benefits of using PLC technology often outweigh the upfront costs in terms of performance and scalability.
In summary, the comparison between FBT and PLC splitters reveals distinct advantages and limitations. For small-scale networks, the cost-effectiveness and simplicity of FBT splitters make them a practical choice. Conversely, PLC splitters excel in large-scale deployments due to their precision and wide splitting ratios. Recommendations vary based on network size: opt for FBT for budget-friendly solutions or choose PLC for extensive signal distribution needs. Looking ahead, the future of optical splitters lies in innovative technologies like Planar Lightwave Circuits, ensuring efficient data transmission across diverse network architectures.
Real-World Applications of PLC Splitters
Demonstrating the Practical Significance of Choosing Appropriate PLC Splitter Configurations
Ensuring Adequate Distribution of Optical Signals Without Compromising Signal Strength
See Also
Never Miss These Fiber Optic Terminal Box Features
Discover the Fascinating World of ADSS Fiber Cable: Everything You Need to Know
Boost Your Fiber Network: Top Strategies for ONU Performance Optimization
Inside the Future of Network Infrastructure: MPO Jumpers Unveiled
Discovering the Heart of ADSS Fiber Cable: Reliability, Efficiency, and Innovation
About US
Follow Us
AnetFiber company's main products are indoor and outdoor optical fiber cables, outdoor waterproof pre-connected fiber-to-the-home products, PLC optical fiber splitters, optical fiber jumpers and pigtails, MTP®/MPO high-density big data product solutions, optical fiber field quick connectors and research and development molding, injection molding and production of optical fiber distribution boxes, optical fiber chassis cabinets, the market has expanded to the world, Europe, America, Asia, the Middle East and Latin America.
Address
Shenzhen City, Baoan District, Yanluo Street, Tangxiayong Community, Yangyong Industrial Road, Tonggangda New Energy Vehicle Park 406
Contacts
+86 199 2655 3586