Comparing FTTH Network Architectures: Advantages and Disadvantages
FTTH Overview
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) networks play a crucial role in providing fiber optic broadband directly to homes and businesses, enabling the delivery of high-speed internet. This technology ensures that users can access reliable and fast internet connectivity, supporting various online activities such as streaming, video conferencing, gaming, and remote work. FTTH networks are designed to bring the benefits of fiber optics directly to end-users, offering an efficient and robust solution for meeting the increasing demand for high-speed internet access.
Did You Know: FTTH networks are capable of delivering symmetrical upload and download speeds, making them ideal for applications that require high bandwidth in both directions.
Design and Deployment
Architectural Design Principles
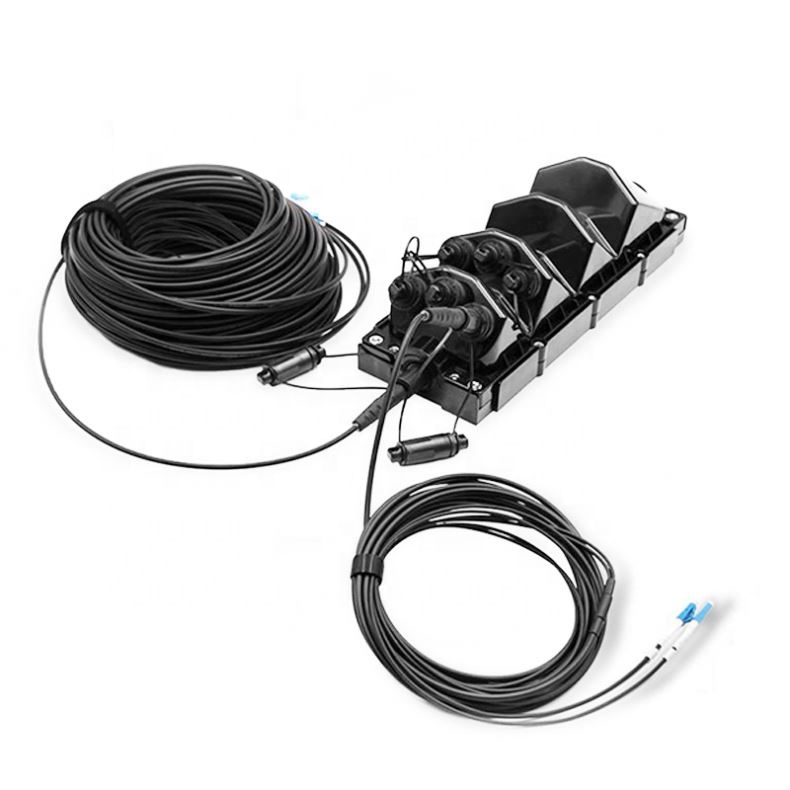
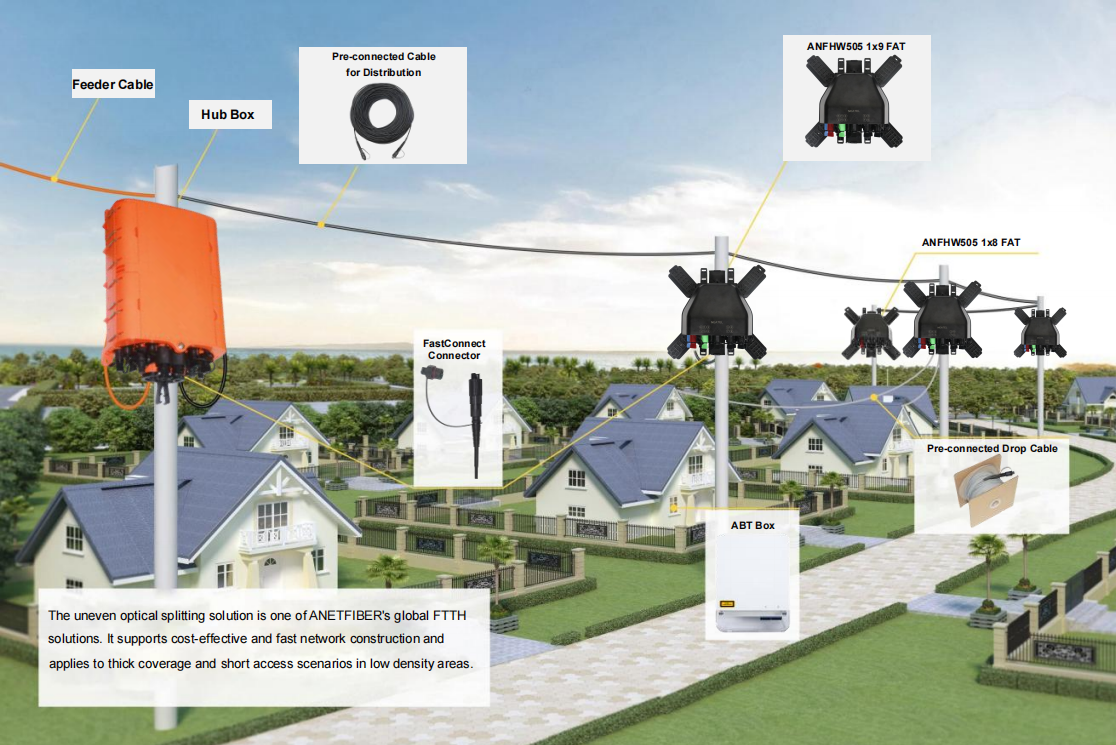
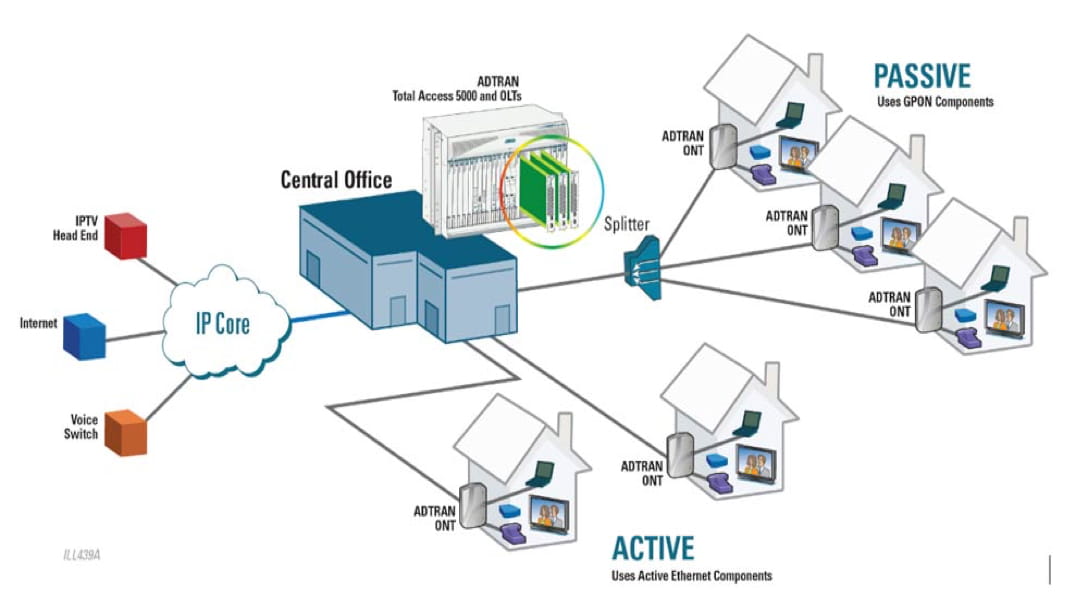
When considering the architectural design of FTTH networks, it's essential to evaluate the various network architectures and their impact on user experience. Different architectural designs can affect factors such as network reliability, scalability, and overall performance. For instance, a point-to-point architecture offers dedicated connections between the service provider's central office and each customer's location, ensuring consistent high-speed internet access. On the other hand, a passive optical network (PON) architecture allows multiple customers to share the same optical fiber, which can lead to potential bandwidth limitations during peak usage times.
Understanding these architectural design principles is crucial for optimizing the user experience and ensuring that FTTH networks can meet the growing demand for high-speed internet access.
Deployment Challenges
Deploying different FTTH network architectures presents unique challenges that need to be carefully addressed. Each architecture comes with its own set of requirements for installation, maintenance, and upgrades. For example, while point-to-point architectures may offer superior performance, they often require more extensive cabling and infrastructure investments. On the other hand, PON architectures require careful planning to ensure efficient resource allocation and minimize potential bandwidth contention among users.
Navigating these deployment challenges is essential for successfully implementing FTTH networks and delivering reliable high-speed internet connectivity to end-users.
Cost and Scalability
Cost Analysis
When comparing the cost implications of different FTTH network architectures, it's essential to consider the initial investment required for deployment as well as the long-term operational costs. The cost analysis involves evaluating factors such as equipment expenses, installation costs, and ongoing maintenance expenditures. For instance, point-to-point architectures often involve higher upfront expenses due to the dedicated connections required for each customer. On the other hand, PON architectures may offer a more cost-effective solution initially, but they can incur higher operational costs over time due to shared infrastructure and potential bandwidth limitations.
Understanding the cost implications of various FTTH network architectures is crucial for service providers and operators to make informed decisions regarding the most economically viable solutions for delivering fiber optic broadband and high-speed internet access.
Scalability Considerations
Assessing the scalability of various FTTH network architectures involves analyzing their ability to accommodate future growth in user demand and technological advancements. Scalability considerations encompass evaluating factors such as network capacity expansion, flexibility in accommodating new services, and ease of upgrades. Point-to-point architectures are known for their scalability due to dedicated connections that can be easily expanded by adding new fibers. Conversely, PON architectures may face scalability challenges as they rely on shared infrastructure, potentially requiring substantial upgrades to meet increasing demands.
Evaluating the scalability considerations of different FTTH network architectures is essential for ensuring that they can effectively support growing needs for high-speed internet while remaining adaptable to future technological developments.
Advancements and Reliability
Technological Advancements
Recent technological advancements in FTTH network technologies have significantly contributed to enhancing the reliability and performance of fiber optic broadband and high-speed internet access. These advancements include innovations in optical networking equipment, transmission technologies, and network management systems. By leveraging these technological developments, service providers can offer more robust and efficient FTTH networks, ensuring a seamless user experience.
One notable advancement is the evolution of Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) technology, which has enabled higher data transmission rates and improved bandwidth utilization within FTTH networks. GPON technology allows for the efficient allocation of bandwidth among multiple users, optimizing network performance during peak usage periods. Additionally, advancements in optical fiber manufacturing have led to the development of bend-insensitive fibers, enhancing the durability and reliability of FTTH infrastructure.
Technological advancements have played a pivotal role in overcoming previous limitations and elevating the reliability of FTTH networks to meet the ever-increasing demand for high-speed internet access.
Network Reliability
Assessing the reliability of different FTTH network architectures is essential for ensuring consistent and uninterrupted high-speed internet connectivity for end-users. The reliability of an FTTH network is influenced by factors such as equipment quality, network redundancy, and fault tolerance mechanisms. Point-to-point architectures often boast higher reliability due to dedicated connections that minimize potential points of failure along the network path.
Conversely, passive optical network (PON) architectures rely on shared infrastructure, which can introduce vulnerabilities in terms of reliability during peak usage times or in the event of component failures. However, advancements in PON technology have led to improved fault detection mechanisms and redundancy features, enhancing overall network reliability.
Customer and Regulatory Impact
Customer Experience
The choice of FTTH network architecture can significantly impact the overall customer experience in terms of internet reliability, speed, and service quality. Different architectures may offer varying levels of performance and stability, directly influencing how users interact with fiber optic broadband and high-speed internet services. For instance, a point-to-point architecture, with its dedicated connections, can deliver consistent and reliable high-speed internet access to individual customers. This setup ensures that users experience minimal disruptions and optimal speeds, enhancing their overall satisfaction with the service.
On the other hand, a passive optical network (PON) architecture, while cost-effective and efficient in its shared infrastructure approach, may lead to occasional fluctuations in internet speed during peak usage times. This fluctuation could potentially affect the customer's online activities and user experience. Therefore, understanding the impact of different FTTH network architectures on customer experience is crucial for service providers to tailor their offerings to meet user expectations effectively.
Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory implications play a vital role in shaping the deployment and operation of various FTTH network architectures. Government regulations and industry standards often dictate the requirements for network infrastructure deployment, service quality benchmarks, and consumer protection measures. These regulations aim to ensure fair competition among service providers while safeguarding consumer interests regarding access to reliable high-speed internet services.
Additionally, regulatory considerations encompass issues such as data privacy, security protocols, and compliance with telecommunications laws. Service providers must navigate these regulatory landscapes when designing and implementing FTTH networks to ensure adherence to legal requirements and industry standards.
Understanding the regulatory implications and considerations associated with different FTTH network architectures is essential for ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations while delivering high-quality fiber optic broadband services to end-users.
FTTH Future Prospects
As FTTH networks continue to evolve, their future prospects are shaped by the ongoing advancements in technology and the increasing demand for high-speed internet connectivity. The complexities and benefits of FTTH networks position them as a pivotal component of the digital infrastructure landscape, offering unparalleled capabilities for delivering fiber optic broadband directly to end-users.
The future of FTTH networks hinges on the seamless integration of emerging technologies to further enhance reliability, scalability, and performance.
As the demand for high-speed internet continues to surge, FTTH networks are poised to play a central role in meeting the evolving needs of residential and commercial users.
FTTH networks represent a transformative force in enabling robust and reliable high-speed internet access, driving innovation across various industries.
The continuous development and optimization of FTTH network architectures will be instrumental in ensuring that they remain at the forefront of delivering superior fiber optic broadband services while addressing the dynamic requirements of modern connectivity.
See Also
Understanding FTTH Network Architecture and Fiber Optic Terminal Boxes
The Impact of Fiber Optic Fast Connectors in FTTH Networks
The Impact of FTTH, FTTN, FTTC, and FTTP in Fiber Optic Solutions
Understanding Fiber Optic Technology: Explaining FTTH and Its Significance
About US
Follow Us
AnetFiber company's main products are indoor and outdoor optical fiber cables, outdoor waterproof pre-connected fiber-to-the-home products, PLC optical fiber splitters, optical fiber jumpers and pigtails, MTP®/MPO high-density big data product solutions, optical fiber field quick connectors and research and development molding, injection molding and production of optical fiber distribution boxes, optical fiber chassis cabinets, the market has expanded to the world, Europe, America, Asia, the Middle East and Latin America.
Address
Shenzhen City, Baoan District, Yanluo Street, Tangxiayong Community, Yangyong Industrial Road, Tonggangda New Energy Vehicle Park 406
Contacts
+86 199 2655 3586